Paradigm shift in medical simulation, from traditional use to a multifaceted societal impact
By: Dr. Nabil Zary – Director – Institute for Excellence in Health Professions Education and Sharon Mascarenhas – Simulation Educator.
Simulation is a method in which the learners gain artificial and virtual experience in an activity that reflects real-life circumstances without taking the risk of real-life situations. Simulation offers an important route to safer care for patients and does so by improving performance, reducing errors, and strengthening teamwork.
The use of simulation in healthcare dates back to many centuries, where anatomical models were used to teach anatomy. In the 20th century, Asmund Laerdal came out with Ressusi-Anne, which was a result of collaborative work of anaesthetists and the industry. This manikin became an example for other models and designs in terms of resuscitation and basic skills education. Current practices of simulation used in healthcare include role-playing with simulators, simulated patients, computer-based simulation, simulation software, videos, DVDs, or creating virtual reality, computer-controlled simulators, and interactive patient simulators. Simulation-based education is a context that uses adult education principles effectively and appeals to different learning preferences. In these contexts, needs are defined by the learner and educator, and where the learners are engaged in learning by doing experiences.
The Khalaf Ahmed Al Habtoor Medical Simulation Centre
The Khalaf Ahmed Al Habtoor Medical Simulation Center at the Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences was established in 2011 and is the largest centre in the UAE.
The Simulation Centre is a society of simulation in healthcare. It is a fully accredited medical education and training facility, equipped with hospital-grade equipment to support healthcare professionals by providing an authentic environment to practice. It features part-task trainers, low medium and high-fidelity manikins to simulated participants, equipped with realistic environments, excellent moulage concepts, and clinical know-how.
The primry aim is to improve skills in patient care by creating a patient journey from pre-admission to discharge, showcasing realistic hospital environments and a clinical skills lab, to better educate student learners and the wider medical community.
Comprehensive and inclusive medical simulation
Beyond the expected scope of medical simulation centres focusing on training health professionals, our 360 Medical Simulation paradigm objective is two-fold: (i) Innovate in the use of simulation for health professionals (ii) Provide simulation-based learning opportunities to the community at large.
Impacting learning of in training healthcare professionals
Designed to support the education of healthcare professionals, the Simulation Centre provides 11 realistic hospital environments for students to learn and practice new techniques and patient care. Currently, simulation-based education is embedded right from the inception in the year 1 of the MBBS programme and the postgraduate Dental Programme. Future healthcare professionals are exposed to the full range of environments beginning from accident and emergency to consultation room experiences where they can learn and practice technical skills such as physical examination as well as non-technical skills like communication and courtesy.
Impacting practice of working healthcare care professionals
Over the years, multiple courses have been designed to serve the needs of various healthcare professionals ranging from school nurses to anaesthesia technologists. Infection prevention and control, mental health assessments, identification and management of acute emergencies in children are a few examples of the varied courses that are conducted for continuous professional development purposes among healthcare professionals. All these courses along with a theoretical component have a rigorous simulation exposure thus enabling the participant to physically and emotionally experience what he or she would do in the exact situation.
Introducing children to the healthcare environments
The first of its kind in the UAE, the Teddy Bear Hospital, was created to promote healthcare awareness and help children overcome their fear and anxiety of visiting a hospital. The Teddy Bear Hospital allows children to experience the journey of going to a hospital, along with their Teddy Bear, where treatments are carried out by healthcare professionals in patient wards and operating rooms. The children are dressed in white coats and are allowed to perform a general check-up on their bear; some of the bears are also chosen by the simulation staff to be examined in the respective areas. They can choose to play the role of a parent or help as a doctor and watch the medical procedures from a different perspective. The final wind up is with an interactive teddy bear game.
Inspiring high school students to become health professionals
The Destination Medicine@MBRU aims to encourage students interested in medicine and health sciences to visit the simulated hospital environment, interact with healthcare professionals, and learn Basic Life Support Skills. The students are oriented to the simulation environment and exposed to various components, not limited to vital signs, equipment used in an operating room, and are also involved in a simulation scenario. The Family & Friends component from the American Heart Association module is also covered during this session.
Opening the door to prospective healthcare students
Pulse Day is a programme that introduces high school students to the medical field through a series of activities, including medical lectures, exploring the research labs, and the Simulation Centre. Students get the opportunity to experience simulated medical scenarios and more.
Engaging our citizens in the training of future health professionals
People from the community who are interested in contributing to the development of healthcare professionals may be chosen to work as Simulated Patients. These individuals are carefully selected and trained to portray a real patient to simulate a set of symptoms or problems used for healthcare education and research. MBRU has a bank of 100+ simulated patients from 21 different nationalities and varying age groups
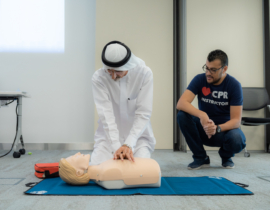
Enabling our citizens to save lives
The majority of cardiac emergency survivors attribute their second chance in life due to immediate life-saving measures, especially early CPR offered by bystanders. At MBRU, we train the community on how to perform Hands-Only CPR – so that they can help deliver life-saving care until professional responders arrive.
Moving forward
Immersive learning to provide simulation-based experiences beyond the physical borders of the centre and novel simulation modalities.
- Take the simulation to the community (in situ).
- Take a larger responsibility to support other centres through the training of their medical simulation professionals.
- Place Dubai as a global hub for medical simulation.